AMD’s Ryzen 3 and Intel’s Core i3 processors are aimed at entry-level users. They’re designed to power effortless multitasking while conserving battery life. If you’re planning a high-performance PC while on a budget, look no further than these new Ryzen processors or Intel’s latest i3 processors.
Together with the RAM, the processor is the most important component of your laptop. Picking the right one for your setup will be crucial for how happy you will be with the performance of the laptop.
But how does the Intel Core i3 compare to the AMD Ryzen 3, both of which target the same market segment? We will be comparing all aspects of the entry-level processors from Intel and AMD.
Comparison Ryzen 3 vs Intel i3
It is really hard to compare these two types of processors because they have a lot of similarities and they are practically in the same ring. Which one is better? This is a bit of an unfair question because there are different versions and generations of both i3 and Ryzen 3 processors. As we listed earlier, there are three generations of AMD Ryzen 3 and twelve generations of Intel i3. So, if we want to compare i3 and Ryzen 3 we should compare multiple products that are released in the same year. For example, the AMD Ryzen 3 3300X has 4 cores and 8 threads, with a base clocking speed of 3.8GHz, and a max of 4.3GHz.
The most likely comparison to this model would probably be the newer 12th Gen Intel Core i3 12300 processor, which also has 4 cores, 8 threads, and a base speed of 3.5GHz. However, this processor has a max frequency of 4.4GHz, so a little more than the Ryzen comparison.
In general, an AMD Ryzen 3 processor is going to be better than an Intel i3 processor across the board. They have more cores, and most of their Ryzen 3 processors have 2 threads for every core. So, as a whole range, you’d likely be better off opting for the AMD.
Aside from directly comparing models to one another, the AMD Ryzen range as a whole has seen a massive increase in use over the last decade. This is because they tend to provide better value as a whole, and what once was an Intel-dominated market, is now more of a level playing field.
Having a multi-core processor with a lot of threads is important nowadays. Most games are multi-threaded, so they rely on your CPU to have enough threads, as well as enough physical cores too.
Clock speeds
Of course, when comparing processors, the most important category to consider is their performance. It is called a clock rate or clock speed and is measured in GHz. There are many Ryzen 3 and Core i3 models on the market, so we’ll take a look at the most popular ones. When looking at an AMD Ryzen 3 1200, it has a base clock rate of 3.1 GHz, which means that the clock of the processor does 3.1 billion cycles per second. On the other hand, the Intel Core i3-4150 has a clock rate of 3.5 GHz, making it a bit faster than the mentioned Ryzen 3 model.
We also have to consider their overclocking performances, as many users regularly overclock their processors to enable better performance. The Ryzen 3 1300X can hit up to 3.95 GHz clock speed once overclocked, which is 250 MHz more than the Turbo Core specifications. What was even more impressive is that this feat was achieved across all 4 cores at the same time.
When it comes to the Core i3-7350K, the overclocked speeds are around 4.8 – 5.0 GHz, depending on the activity you’re performing. Looking at these results, we can see that the Intel i3 processors usually have the Ryzen 3 models beat when it comes to clock speeds, but this is not the only way to compare their performance.
Threads
The other thing to consider when talking about performance, besides the clock speed and the number of cores, has to be the number of threads. To simply explain it, the number of threads is equal to the number of cores the processor thinks it has. In most cases, laptops have 2 threads of every core, which lets them balance the workload between different cores. There are also laptops with only 1 thread per core, but you should aim for those with 2, as it improves the performance significantly.
In our case, the AMD Ryzen 3 1300X processor has only 1 thread per core, whereas the Intel i3-7350K has the same number of threads – 4, while only having 2 cores. As there are many Ryzen 3 and Intel i3 models available, you would need to look into them as some of them are single-thread and others are multi-thread.
Power Consumption
Power Consumption is another thing that can impact a processor’s performance. If the processor draws too much power, not only would the battery last less, but the CPU would get very hot and that can negatively impact its future performance. Over the last few years, AMD has dominated this category, as its processors were much more power-efficient than their Intel competitors.
Let’s first take a look at Intel Core i3-7350K. While at idle conditions, it consumed a little below 5W, which is great for a processor of this caliber, as there was no background activity at all. Once overclocked, at 4GHz the power consumption was around 6.2W, while at 5GHz it was around 7.5W. The fact that it never crossed 8W makes it a quite efficient power draw for a CPU.
Now, when it comes to the AMD Ryzen 3 1300X it consumed a little below 4W while under idle conditions, which is good even for AMD processors. It’s a whole different story when overclocked though, at 4GHz the power consumption jumped to 12.8W, way more than the Intel processor at 5GHz. All in all, AMD was better in idle conditions, whereas Intel had an advantage once overclocked.
AMD Ryzen 3 – Specs And Performance
First of all, if we want to talk about the Ryzen 3 specifications and performance, we have to say that there are 3 different generations of AMD processors. The first one was introduced in 2017 and the last (3rd) generation in the middle of 2020. Each Ryzen 3 processor from every generation has different specifications, so we should explain every one of them.
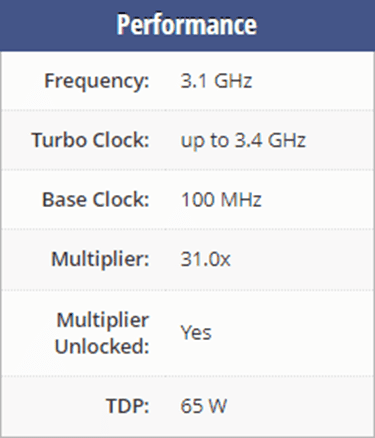

The first generation was introduced in 2017 and as we expect it is the oldest generation. The best example of this generation is the Ryzen 3 1200. It is a desktop processor with 4 cores using the Zen architecture with Socket AM4. Ryzen 3 1200 has 8MB of L3 cache and operates at 3.1 GHz by default, but can boost up to 3.4 GHz, depending on the workload.
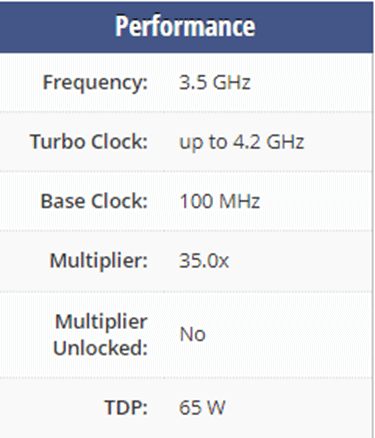

The second generation doesn’t have that much of an improvement compared to the first, but it’s a little bit faster. When we talk about the second generation we should talk about Ryzen 3 2300X. Like the one we talked about in the first generation, Ryzen 3 2300X also has 4 cores but it’s using Zen+ (Pinnacle Ridge) architecture Socket AM4. Ryzen 3 2300X has 4MB of L3 cache and operates at 3.5 GHz by default, but can boost up to 4.2 GHz, where we can see an improvement.
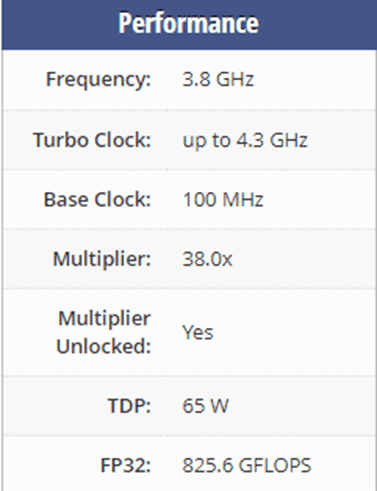

The latest generation where we can see a Ryzen 3 is the third generation. There we have the Ryzen 3 3300X which is currently the best processor in the Ryzen 3 series that AMD has released. Ryzen 3 3300X has 4 cores and it’s using the Zen 2 (Matisse) architecture with Socket AM4. Thanks to AMD Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) the core count is effectively doubled, to 8 threads. Ryzen 3 3300X has 16MB of L3 cache and operates at 3.8 GHz by default, but can boost up to 4.3 GHz.
Intel Core i3 – Specs and performance
Like AMD, Intel also has different generations and different types of processors. Intel i3 has 12 generations of processors. The first one was released in January of 2010 and the latest in January 2022, so we can say that Intel has been producing i3 processors, actively, for the last 12 years. Because there are more than 30 different types of Intel i3 processors we won’t talk about every one of them.
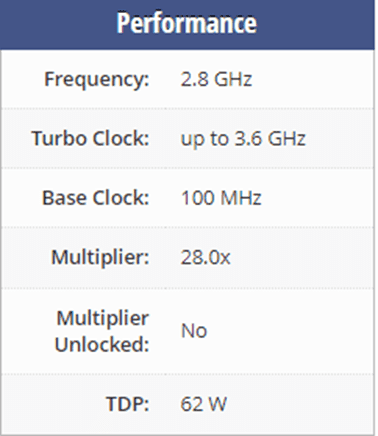

We can start with Intel i3 8100 as it’s released in October 2017, and it can be compared to Ryzen 3 1200 (which has also been released in 2017). Intel i3 8100 has 4 cores and it’s using the Coffee Lake architecture with Socket 1151. Core i3-8100 has 6MB of L3 cache and operates at 2.8 GHz by default, but can boost up to 3.6 GHz, depending on the workload.
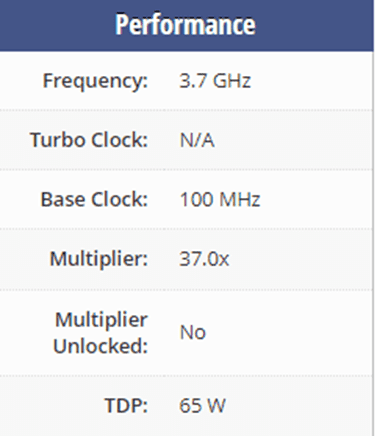

The second i3 processor that we should talk about is the Intel i3 9100. It’s the 9th gen. and it was released in 2018 (the same year as AMD Ryzen 3 2300X). Like i3 8100 it also has 4 cores and it also uses the Coffee Lake Refresh architecture with Socket 1151. Also, both of them have 6MB of L3 cache.
The big difference i3 9100 made compared to i3 8100 is in their base speed, as i3 9100 operates at 3.7 GHz which is a lot faster compared to the 2.8GHz that 8th has. However, i3 9100 doesn’t have the option to overclock so their speed is limited to 3.7GHz, and compared to the overclocked 8th gen, they are practically the same.
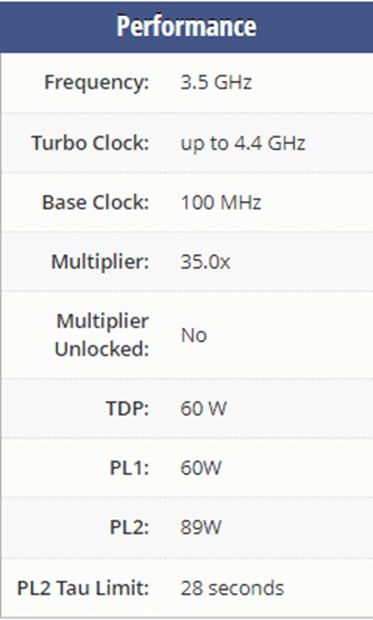

Finally, the newest intel i3 processor (from 12th generation) and currently the best product from the i3 series is the Intel i3 12300. It works with 4 cores and it’s launched in January 2022. It is part of the Core i3 lineup, using the Alder Lake-S architecture with Socket 1700. Thanks to Intel Hyper-Threading the core count is effectively doubled, to 8 threads. Core i3-12300 has 12MB of L3 cache and operates at 3.5 GHz by default, but can boost up to 4.4 GHz.
Conclusions
All things considered, there isn’t a clear winner when comparing these 2. There are many versions of both the Intel i3 and the Ryzen 3 processors, so the answer heavily depends on which exact models you’re comparing. Ryzen 3 models are perfect for all gamers who are on a relatively low budget, as they can rival Intel’s performance in almost all multi-threaded applications. Although if you’re on a really strict budget, the Intel Core i3-7100 may be the best option, as it has an integrated GPU which the Ryzen 3 doesn’t.
On the other hand, if we take a look at power consumption, Intel models perform way better, as they usually draw much less power if you’re doing any kind of activity. AMD only outperforms it under idle conditions, which doesn’t occur that often in day-to-day use. Even though it uses a lot of power, its performance more than makes up for it. In all multi-threaded benchmarks, the Ryzen 3 always comes out on top, only losing when it comes to single-threaded benchmarks where Intel completely dominates it.
The only category which was completely one-sided was the gaming benchmarks. Intel’s processors were ahead of AMD ones, no matter the title. It doesn’t tell the whole story of course, as games heavily depend on the GPU as well, but Intel always being better certainly proves a point.

